Abstract
Background
A significant portion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients (35-40%) relapse or are refractory to frontline chemotherapy. The standard of care for relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL patients has been salvage chemotherapy followed by consolidation with autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) in eligible patients. Epigenetic alterations, such as aberrant DNA methylation patterns, have been linked to chemotherapy resistance in DLBCL. CC-486 is an oral hypomethylating inhibitor that inhibits DNA methyltransferase, and has provided evidence for chemotherapy sensitization in DLBCL (Clozel T, et al. Cancer Discovery, 2013). This provides rationale for addition of CC-486 to standard cytotoxic chemotherapy rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (R-ICE) in R/R DLBCL patients who are candidates for ASCT. Here we report the results of the phase 1 trial investigating this combination.
Methods
Eligibility included age ≥ 18, a diagnosis of R/R DLBCL, follicular lymphoma grade 3B, or DLBCL transformed from indolent lymphoma who were candidates for salvage chemotherapy and ASCT consolidation. The study was conducted via standard 3+3 dose escalation of CC-486 at 200 mg (dose level (DL) 1), 300 mg (DL 2), and 150 mg (DL -1). A Dose limiting toxicity (DLT) was defined as grade ≥ 3 adverse event (AE) as defined by CTCAE v5 leading to ≥ 7 day delay in cycle (C) 1 or 2 of R-ICE chemotherapy as well as grade ≥ 2 vomiting/diarrhea, persisting 48 hours despite best supportive care. Patients received up to three 21-day cycles. CC-486 was given as a 7 day lead in prior to C1 and then on days 8-21 of C1 and C2 with doses held based on cytopenias/AE's per protocol. G-CSF was mandated with each cycle. The primary objective was to determine the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of CC-486 in combination with R-ICE chemotherapy. Secondary objectives included overall response rate (ORR)/complete remission (CR) per 2014 IWG criteria, peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) collection feasibility, and proportion of patients receiving ASCT consolidation. Biomarker objectives included assessment of locus specific and global methylation patterns in ctDNA at set time points.
Results
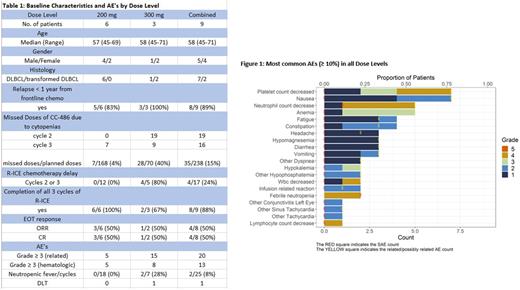
The study has completed accrual with enrollment of nine patients from two institutions, all of which completed planned therapy. Eight (89%) of the patients had relapsed < 1 year from completion of frontline chemotherapy. Six patients were treated at the DL1 (200 mg), three patients were treated at DL2 (300 mg), and zero patients were treated at DL-1 (150 mg) with baseline characteristics described in table 1.
The most common AE's (figure 1) included nausea (78%), thrombocytopenia (78%), anemia (56%), neutropenia (55.6%), fatigue (44%), and constipation (44%).
Compared with DL1, DL2 was associated with greater incidence of grade ≥ 3 hematologic AE's/cycle including neutropenia (42% v 6%), anemia (29% v 11%), and thrombocytopenia (42% v 6%); higher incidence of neutropenic fever/cycle (28.5% vs 0%); more frequent delays in day 1 of C2 or C3 of R-ICE chemotherapy (80% vs 0%); and higher rate of CC-486 doses missed in C2 and C3 due to cytopenias (40% and 4%) respectively. One DLT occurred at DL2 in a patient with grade 5 neutropenic sepsis. A planned safety review of the three patients at DL2 established that no further patients would be enrolled at this dose. No DLTs were noted in the six patients enrolled at DL1.
The ORR(CR) of the 8 evaluable patients was 50%(50%) and 4/9 patients proceeded to ASCT. With a median follow up of 9.5 months (range 1.2-25.1) the median PFS and OS were 4.0 months (95% CI 2.1-NR) and 10.7 months (95% CI 9.5-NR) respectively. All 4 patients successfully collected PBSCs (defined as ≥ 3.0 x 10^6 CD34 cells/kg) with median of 4.08 x 10^6 cells/kg. Biomarker studies are pending.
Discussion
Patients enrolled at DL1 (200 mg) tolerated this combination well with expected hematologic AE's, no episodes of neutropenic fever, few missed doses of CC-486, no delays in R-ICE chemotherapy, and no DLTs. The CR rate was 50% and a high proportion of patients (89%) enrolled after relapsing < 1 year from completion of frontline therapy. Biomarker studies may provide information regarding DLBCL populations likely to benefit from combinations of chemotherapy and epigenetic priming. Biomarker studies related to locus specific and global methylation patterns in ctDNA will be presented at the ASH conference.
Hess: BMS: Speakers Bureau; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy. Cerchietti: Celgene: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Hill: Eli Lilly and Company: Ended employment in the past 24 months.